Reimplementation of Burrows-Wheeler Transformation for genome wide sequence data compression
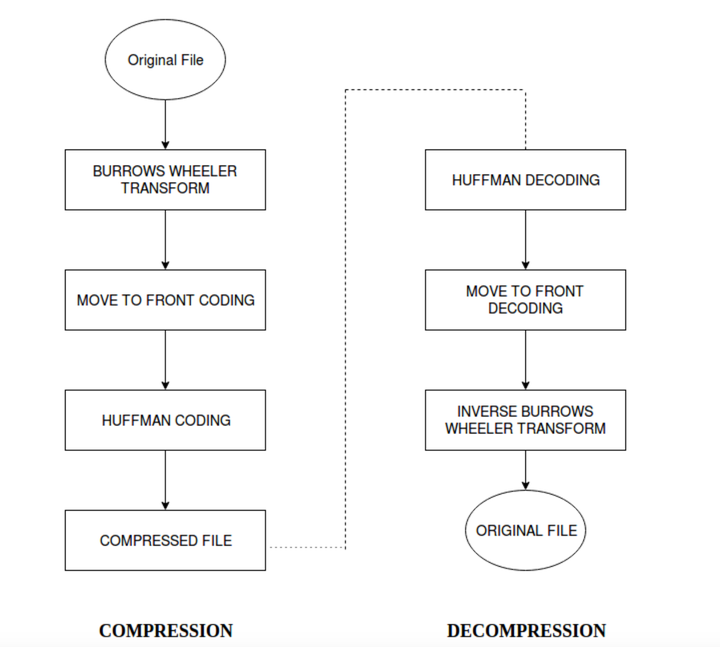
With the advancement in sequencing technology the cost of sequencing has seen a huge fall in terms of cost. Companies like Illumina offer whole genome sequencing for as less as five thousand US dollars. The sequence dataset of large scale projects like 1000 genome projects, which aim at sequencing the genomes of several thousand humans and determining the genetic variants with at least 1% frequency, contains around 6 trillion base pairs. Along with humans, other species’ genomes are also being sequenced. The large amount of data produced by sequencing methods makes it difficult to store and transfer the data. The compression ratio achieved by Burrows-Wheeler Transform have been compared against the compression achieved by gzip. Gzip is the de-facto compression method used by Unix. Input given to software is human genomic data. The file sizes are in MB. The overhead incurred for the BWT is due to the dictionary of Huffman codes. Since the dictionary consists of just 4 nucleotide characters and their codes, it is negligible and can be ignored.