admin
Biography
Experience
Data Scientist
Reliance Jio, AI Centre of Excellence
- Co-Occurrence Based Genome Wide Association Study (CO-GWAS) System
- Rapid Digital Twin for Crude Oil Refineries
- Complexity Based Sampling from Black Box models
Research Intern
SciWhy Lab, School of Computational and Integrative Sciences, JNU
- Prediction of DNA and RNA binding proteins from protein sequences
- Compression tool for gene sequences
Master’s Thesis Student
Department of Biological Sciences, BITS-Pilani
- Prediction of CRISPR regulated self-target genes in Salmonella Typhimurium
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) data analysis using Persues and MaxQuant.
Project Assistant
Indian Institute of Science
- Vehicular Traffic Parameters Estimation
- Manual data labelling, negotiating with stakeholders for GPU systems, getting cameras fixed on roads, training YOLO models for object detection
Projects
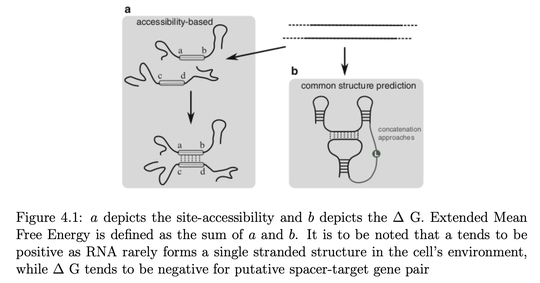
CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is an immunity system that was discovered in E. Coli. The CRISPR system consists of short repeats of palindromic DNA which is interspaced by non identical spacer sequences.
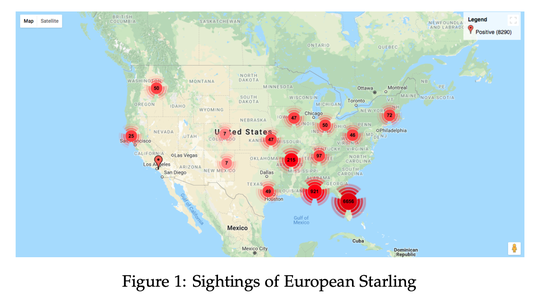
In the past few decades, a number of methods have been proposed to model species distributions yet there is no goto approach for applied researchers to model a given species. Given the publicly available datasets of detailed climatic and topological data along with the effort and collaboration of researchers to generate reliable location data of different species, predictive modelling of species distribution has become substantially feasible and reliable.
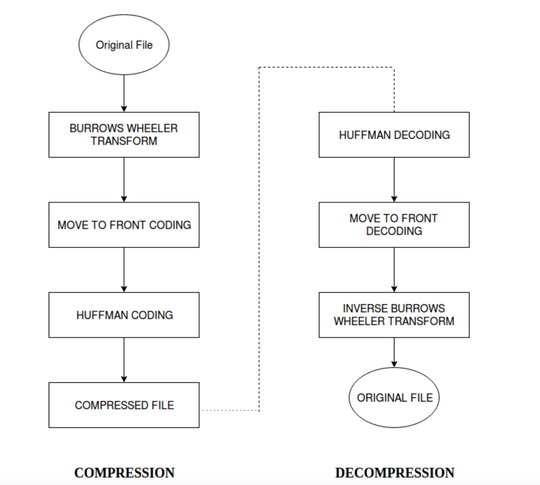
With the advancement in sequencing technology the cost of sequencing has seen a huge fall in terms of cost. Companies like Illumina offer whole genome sequencing for as less as five thousand US dollars.
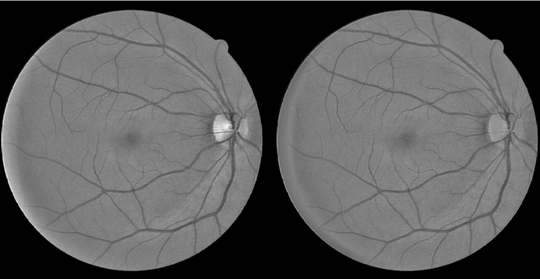
This algorithm is based on the work of Nguyen et. Al. The idea behind this approach is that the blood vessel structures can be approximated as piecewise linear, so line detection on multiple scales can be used to separate the blood vessel structure from the background.
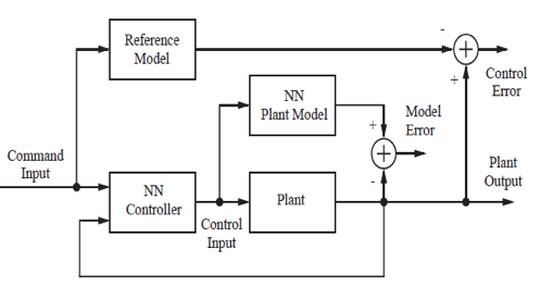
This paper proposes a neural network control scheme of a DC-DC buck-boost converter using model reference control. In this technique, a dynamic back propagation algorithm is used. The controller is designed to stabilize the output voltage of the DC-DC converter and to improve performance of the Buck-Boost converter during transient operations.
Contact
- palash1995.18@gmail.com
- (+91)8839919481
- 570, Shaktinagar, Jabalpur, India 482001
- DM me on Twitter!